Benefits of Using EC Fans vs AC Fans in Data Center Applications
Many companies require a location to house the physical aspects of their technology networks, servers, telecommunications, and other equipment. While the location may consist of an IT room or computer closet in the building, other companies rely on data centers. Data centers are facilities that provide storage capabilities for computer systems and related components including firewalls, routers, and switches.
Data centers may consist of one building or multiple buildings depending on the needs of the company. All the equipment requires electricity to operate as the running equipment also generates large amounts of heat (Figure 1). This heat may cause equipment issues and malfunctions that could create service disruptions as the equipment requires cooling systems. When it comes to running electrical and cooling systems, a data center may run into enormous costs.

Figure 1: Example of a data center running numerous equipment.
Costs for a data center depends on the size of the building and the amount of technology and equipment stored in the facility. Operating the cooling and ventilation systems make up roughly 40% of total electricity costs. This figure may equal to or even surpass the electrical expenses used to power the technology in the data center. In addition, the cooling system may also cost more than the value of the equipment itself.
Removing the cooling equipment from data centers is not an option. However, investing in components that efficiently use electricity while still providing the same conditioned air performance is essential to keep systems running optimally. Deciding between EC vs. AC fan/motor technology for the fans may offer the ideal option for your data centers.
AC, DC, and EC Fan and Motor Technology
There are various types of motors that can be used to operate cooling fans in data centers. Evaluating the types of motors are based on how they take the electrical energy and then convert this into the appropriate mechanical energy for the fan. Three types of motors are AC, DC, and EC motors.
AC Fans and Motors
Alternating current (AC) induction motors consist of a stator with electrical windings. An alternating input current makes a rotating magnetic field called a stator field. This stator field brings about a current within the conductive rotor to make another magnetic field. Both of these fields create the rotor's torque force for the fan.
Another type of AC motor is called an AC synchronous motor. These motors work with a precision supply frequency as a permanent ring or slip rings are designed to create the magnetic field. They usually run more efficiently than an induction motor.
The thing to keep in mind with an AC fans is that they operate at the motor's peak efficiency when reaching a certain point of their performance curve. If going beyond the performance curve, the efficiency rate drops. To overcome this issue, a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is utilized to increase or decrease the AC supply frequency when necessary.
When compared to other types of motors, AC motor technology is less efficient as it requires more electricity to create the magnetic field with the copper windings.
DC Fans and Motors
Direct current (DC) fans are brushed motors with permanent magnets along the stator. These magnets create a fixed magnetic field that influences the electrical windings of the rotor. These electrical windings are voltage induced. To switch the direction of the direct current, a commutator ring and carbon brushes are used in the design. As the fixed permanent magnets and internal rotor interacts, the motor rotates.
A DC fan is more efficient than an AC fan by about 30%. However, these motors have a shorter lifespan as the wear and tear can cause the components to give off more operational noise. Also, DC power supplies have started to become slowly phased out.
EC Fans and Motors
Electronically commutated (EC) motors.(Figure 2) are similar to DC motors as they are designed with permanent windings and magnets. However, the major difference is that they do not have carbon brushes as the windings are electrically commutated instead of mechanically commutated. A VFD or an electronic circuit board controls the motor.
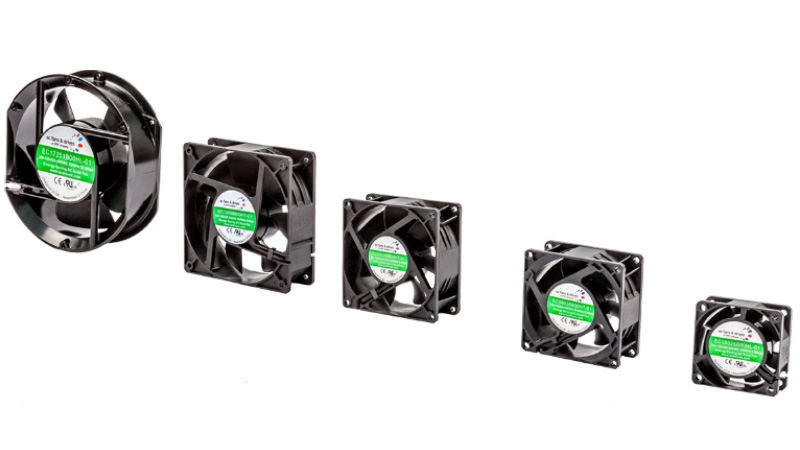

Figure 2: Example of EC axial fans used in data center server racks.
The onboard circuits of the EC motors convert AC power to DC power due to a rectifier. These motors provide the best characteristics of AC and DC motors by providing enhanced performance and longer motor lifespans without operational noises or using additional energy to create the required magnetic fields. Typically, an EC motor is 70% more efficient while using roughly 50% less electricity.
Cost Differences
When it comes to comparing the cost differences between an AC vs. EC fans and motors, AC motors are cheaper. They may cost anywhere from 15% less than an EC motor. However, operational costs are 2 or more times higher for an AC motor while an EC motor lasts longer.
- Example 1: An 4" AC inline fan
- An AC inline fan motor may cost roughly $60 based on the manufacturer while using 60W of power. Operational costs for the AC fan may go up to about $85 per year
- An EC inline fan with an EC motor may cost about $75 to purchase but only use 21W of power. Operational costs for the EC fan may run about $30 per year.
- Example 2: A traditional 120mm x 120mm axial fan
- An AC motor may cost roughly $10.00 based on the manufacturer while using 18W of power. As the AC fan is inefficient, the running cost (based on $ 0.156 KwH) would be approximately $24.60.
- An EC axial fan with same airflow performance with an EC motor may cost about $15 to purchase, would consume approximately 4.5W of power, which equates to the running cost (based on $0.156 KwH), would be approximately $4.73.
When you take the electric running cost ($19.87) and multiply this by several thousand fans in situ at a data center, the overall savings is significant and any additional cost in EC product is returned within a short period of time.
Data Center Applications
When talking about cooling capabilities in data centers, there are several locations where an EC motor may be housed. There may be generalized air conditioning through the HVAC system and centralized cooling along the server racks housing the servers, switches, firewalls, and other equipment.
Server Racks
Server racks are equipped with axial fans that blow the conditioned air from the HVAC center into the rack space. These fans also help to vent the higher air temperatures out of enclosed server racks and away from sitting equipment. Each rack may contain anywhere from 12 to 16 total fans. Roughly 6 to 8 fans are positioned at the bottom of the rack to bring in the cooler air and 6 to 8 fans are up at the top to vent the hot air. This setup increases the air ventilation capabilities inside the server rack.
EC motors may take the place of AC motors in axial fans for these server racks. Installation is easy, as the new EC axial fan is simply dropped into the unit housing. They can be used immediately to begin lowering energy costs.
Potential Operational Cost Savings of Using EC vs. AC
Keep in mind that no changes need to be made to data center power infrastructures if it is using AC power. The EC fans contain brushless DC motors that converts the AC current to DC current. So, data centers operators will not have to redesign the AC power supplies to accommodate for the EC motors.
Initial costs for the purchase of EC motors will be higher than both DC and AC motors. However, the longevity of EC motors over AC motors makes up these cost differences in longer potential savings. This benefit is due to the EC helping to minimize the voltage fluctuations created by AC power supplies. You also gain greater levels of speed control, allowing the EC motor to run at reduced speeds during off-peak hours for data center technologies. So, data centers may obtain efficiency rates of up to 70% with 40% high air flow rates but using roughly 50% less energy.
Summary
Data center operators looking to reduce electricity and cooling costs may find advantages by replacing their AC motors with EC motors in HVAC systems and server racks. An EC motor provides a wider operational range, which allows for more scalable solutions depending on the size and ventilation needs of the facility.